
pZ Vectors

|
pZ Vectors |
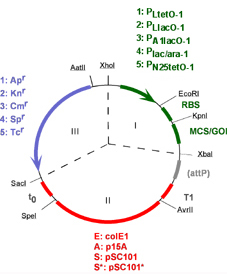
| 1 Architecture of the pZ vector system The pZ vector family comprises three main modules which are in general separated by the unique (see Notes for exceptions) cleavage sites XhoI, XbaI, AvrII, SpeI, SacI and AatII . Module I contains the signals for transcriptional regulation, i. e. promoter/operator constructs as well as a ribosomal binding site (RBS) which both can be exchanged by unique cleavage sites (XhoI(AatII)/EcoRI or EcoRI/KpnI, respectively). This module contains also either a multiple cloning site (MCS) or the luciferase gene which can be replaced by any other gene of interest (GOI). Module II harbors one of four origins of replication (colE1, p15A, pSC101, pSC101*). All replication origins are compatible, except pSC101 and pSC101*. The replication origins are shielded from readthrough transcription by terminator T1 of the rrnB operon and t0 of phage Lambda. pZ vectors suited for integration into the E. coli chromosome carry the attachment site of phage Lambda (attP) in addition. Module III contains one of five antibiotic resistance markers which carry their genuine promoters and ribosomal binding sites (RBS). |
| 2 Topography and sequences of promoters All promoter sequences are flanked by XhoI (ctcgag) and EcoRI (gaattc) cleavage sites (printed in lower case letters). The -10 and -35 hexamers are printed in bold, the transcriptional start site is underlined. lac operators are printed in red, tet operators in blue, ara I1-I2 (the binding site of AraC) is printed in green. "lacOs" is a symmetrical 20 bp synthetic operator. An additional lac operator is located further upstream of Plac/ ara-1 is flanked by an AatII (gacgtc) restriction site. |
| 3 Cloning sites pZ vectors offer either a multiple cloning site (MCS) or the luciferase gene for the insertion of genes to be cloned and/or expressed. Depending on the vector backbone some of the restriction sites are not unique. Please refer to the individual vector sequences (tools & reagents) for more details. |
| 4 Nomenclature of the pZ vector system The letter (E, A, S, S*) denotes the origin of replication. The first digit indicates the resistance marker (1 to 5). The second digit (1 to 5) defines the promoter controlling the gene of interest. The MCS or the description of the gene of interest, e.g. luciferase, follows this code as examplified. |
| Origin of replication |
Resistance marker | Promoter | Expression unit |
Designation of vector (example) |
|||||
colE1 (E) |
Ampicillin (1) |
PLtetO-1 (1) |
MCS |
pZE11MCS |
|||||
| p15A (A) |
Kanamycin (2) |
PLlacO-1 (2) |
luc |
pZA22luc |
|||||
| pSC101 (S) |
Chloramphenicol (3) |
PA1lacO-1 (3) |
MCS |
pZS33MCS |
|||||
| pSC101* (S*) |
Spectinomycin (4) |
Plac/ara-1 (4) |
luc |
pZS*44luc |
|||||
| . | Tetracycline (5) |
PN25tetO-1 (5) |
luc |
pZE55luc |